Explain the Different Types of Isomerism Encountered in Organic Chemistry
Optical isomers which are mirror images of each other and can rotate plane polarised light. Occurs when the atoms in a molecule can be rearranged such that different atoms are bound to one another ie.
Ethyl alcohol and dimethyl ether are isomers of each other as both the compounds have the same molecular formula C2H6O while different structural formulae.

. Isomerism is a concept most often encountered in organic chemistry Topic 20 where there are several different types of this property. - Hybridization of atomic orbitals and geometry of organic molecules. Organic Chemistry Reactions List.
In eclipsed conformation the hydrogen atoms on two carbon atoms are as close as possible. Diastereomers especially the cistrans variety are common isomers encountered in organic chemistry and they are also found in inorganic chemistry. Primary carbons are connected to one carbon only.
THE SHAPES OF MOLECULES. Conformational isomerism involves rotation about sigma bonds and does not involve any differences in the connectivity or geometry of bonding. The intent of this book is to provide the basic concepts of organic chemistry to the students which are new to organic chemistry and the tutors and teachers to provide good material for teaching organic chemistry.
Stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism. Several different types of isomers are possible depending on how the atoms are arranged and what makes two related isomers different Figure 1. Werner proposed that these are two geometric isomers of formula CoNH 3 4Cl 2Cl with.
Each general isomer class can be further subdivided into different types. - Constitutional and conformational isomerism. Tertiary carbons are connected to three carbon atoms.
Compounds with the same stoichiometric formula but different structures. For example the following are some of the constitutional isomers of C. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS I n this chapter we first briefly review the most important types of covalent bonds encountered in organic substances and the ways in which these bonds are represented in structural formulas.
For exemple he explained the existence of two isomers of CoNH 3 4Cl 3 one green and one purple. The free radical Substitution Reaction. The terms cis and trans mean roughly.
Polarity polarisability inductive and mesomeric effects. There are different classifications of stereoisomers but they are often categorized mainly as. As noted in a previous chapter the light our eyes see is but a small part of a broad spectrum of electromagnetic radiation.
Secondary carbons are connected to two carbon atoms. Geometric isomers called cistrans isomers can arise when a double bond or ring is. There are two general types of isomers.
Two or more structures that are categorized as conformational isomers or conformers are really just two of the exact same molecule that differ only in terms of the angle about one or more sigma bonds. You will encounter this notation when starting to learn the functional groups and continue using it in the. There are four different isomers you could make depending on the position of the chlorine atom.
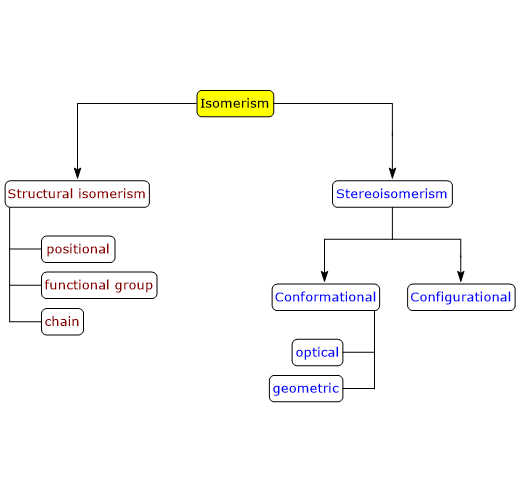
Isomerism is frequently encountered in organic compounds although there are some inorganic compounds which exhibit isomerism. Structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but their atoms are arranged in a different way. Geometric isomers found in alkenes which have two different groups attached to each carbon of the CC.
The portion of the infrared region most useful for. And if four carbons are connected to a carbon then it is a quaternary carbon. The atom connectivity is not the same.
Next we consider the sizes and shapes. 1 constitutional isomers and 2 stereoisomers. 171 Types of Isomerism.
On the immediate high energy side of the visible spectrum lies the ultraviolet and on the low energy side is the infrared. This book contains the basic information about the organic compounds and their chemistry. Compounds such as pentane iso-pentane and neopentane are isomers of each other.
- Stereoisomerism enantiomers diastereoisomers - Electronic effects. These all three compounds have the same molecular formula- C5H12. Any other intermediate conformation is called a skew conformation.
Our aim is to have you. Stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms constitution but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. There is a total of seven types of Organic Reaction.
In one case it is attached to the side-group carbon atom and then there are three other possible positions it could have around the ring next to the latex CH_3 latex group next-but-one to the latex CH_3 latex group or opposite the latex CH_3 latex group. ABC D In contrast in stereoisomers. Geometric isomers and isomers containing an asymmetric center are the two main subcategories of stereoisomers.
In staggered conformation the hydrogen atoms on two carbon atoms are as far apart as possible. You will see that in the chloride ion ligands are in positions adjacent to each other cis to each other in the octahedral arrangement. Nobel Prize for Chemistry 1913 For complexes with more than one type of ligand Werner succeeded in explaining the number of isomers observed.
Isomerism Definition Types Diagrams And Examples
Basic Principles In Organic Chemistry Structural Isomerism Open Teaching Project

Isomerism Definition Detailed Explanation Types Examples Of Isomerism

No comments for "Explain the Different Types of Isomerism Encountered in Organic Chemistry"
Post a Comment